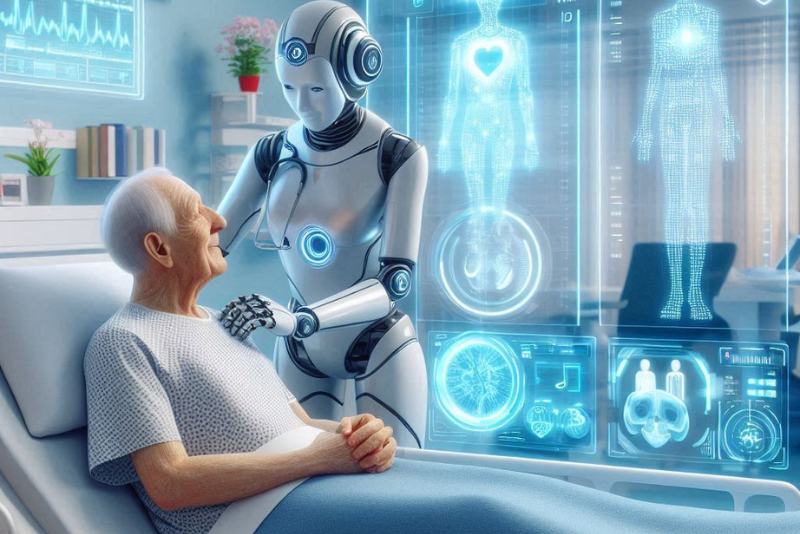
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has developed from a mere smart technology into a transformative force across various industries. Among its many advancements, AI’s integration into healthcare stands out as one of the most revolutionary. The introduction of Generative AI in healthcare, in particular, represents a groundbreaking leap, significantly enhancing patient outcomes and care.
While some adopt AI, others take a ‘wait-and-see’ approach. However, with AI’s transformative potential, now is the time to learn, adapt, and embrace this technology. Among AI’s most promising branches, Generative AI (GenAI) stands out for its revolutionary potential in healthcare. So, would you learn or risk becoming a spectator in this high-speed race for innovation?
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is the development of computer systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as decision-making and problem-solving. AI benefits include improved prediction accuracy, decision-making, problem-solving, and time-saving computations.
You can check this blog to understand AI’s unrealistic impact on healthcare deeply. In summary, AI simplifies complex processes and saves significant time for healthcare professionals. Since the 1950s, when AI was initially named, it has revolutionized industries such as healthcare, marketing, finance, and creative sectors; PwC estimates that AI will contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030. Reasons for the uptake of AI in healthcare include:
- The volume of medical data available.
- Progress in algorithms.
- The capacity to analyze and make decisions based on complex data.
AI in healthcare identifies diseases and helps develop novel treatments and personalized patient care. Generative AI, particularly large language models (LLMs), has impacted healthcare so that executives and researchers are focused on the latest benefits it can bring.

What is Generative AI
Imagine AI as a vast array of instruments, each crafted for a particular function. Machine learning identifies patterns and generates ideas. Deep Learning excels in image recognition and natural language processing. Neural networks simulate brain functions to classify medical images, predict outcomes, and optimize treatments. Generative AI generates novel creations such as crafting narratives, creating artwork, or composing melodies.
Core Concepts
Unlike conventional AI, generative AI creates unique outputs that imitate real-world data rather than simply identifying patterns or forecasting outcomes. Its main feature is its ability to replicate complex data sets.
While AI recognizes things, generative AI creates things using advanced machine learning methods like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
How Generative AI Works
Generative AI functions by analyzing vast amounts of data to understand core patterns and structures. For instance, GANs comprise two neural networks (the generator and the discriminator) that collaborate. The generator creates fake data, while the discriminator compares it to actual data to determine its accuracy. This competitive process motivates the generator to create more authentic results.
There are plentiful real-world examples of Generative AI’s capabilities. In the creative industry, Generative AI can produce artwork or design patterns. In healthcare, it extends to generating synthetic medical images, developing new drug candidates, and personalizing treatment plans based on genetic data.
Use Case Of Generative AI in Healthcare
1. Enhancing Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Medical imaging is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics. Generative AI has significantly advanced this field by improving the accuracy and efficiency of image analysis. GANs and VAEs can generate synthetic medical images that augment limited datasets, enhancing model training and validation. This process helps address data scarcity and improve diagnostic precision.
For example, artificial images can be utilized to improve the accuracy of machine-learning models in detecting abnormalities like tumors or fractures. This new technology helps radiologists improve their evaluations and also assists in creating advanced imaging algorithms for better visualization of minute details.
2. Facilitating Drug Discovery and Development
The process of discovering drugs is well known for being intricate and requiring much time. Generative AI is transforming this area by speeding up the discovery and creation of novel drugs. AI algorithms powered by artificial intelligence can anticipate potential interactions between drugs, examine molecular configurations, and replicate drug actions, ultimately expediting the process of uncovering discoveries.
GenAI enables researchers to examine extensive chemical spaces and detect potential drug candidates by creating virtual compounds and molecules. This method has resulted in treatments designed for individual genetic makeups and disease features, promoting the growth of personalized medicine.
3. Personalizing Medicine
Generative AI is essential in customizing healthcare by using patient information to develop personalized treatment strategies. AI models examine digital medical records, genetic information, and clinical results to create customized suggestions. This feature allows healthcare providers to make educated choices on treatment options, leading to better patient outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
One instance is that AI algorithms can forecast an individual’s reaction to specific treatments by analyzing their genetic makeup and medical history, resulting in improved and tailored therapies.
4. Medical Research and Knowledge Generation
Generative AI helps with medical research by creating fake data that meets specific criteria, which helps address privacy issues related to sharing actual patient information. This fabricated data enables researchers to form fresh theories and model clinical trials without risking patient privacy.
Initiatives such as Simulacrum showcase how synthetic data can be applied in research, offering essential perspectives and promoting creativity while adhering to privacy laws.
5. Content Creation and Hyperpersonalization
In the pharma industry, Generative AI excels in creating personalized content tailored to individual healthcare providers or patients. By generating content variants, AI enhances engagement rates on digital platforms like emails and web ads. This approach improves the effectiveness of marketing and communication strategies, leading to better patient and provider interactions.
6. Automation and Efficiency in Clinical Workflows
Generative AI improves the automation and effectiveness of clinical processes, such as patient intake, treatment planning, and revenue cycle management. By automating administrative tasks, GenAI speeds up processes and reduces errors, enabling healthcare professionals to prioritize direct patient care.
Automation enhances precision and cuts expenses by efficiently allocating resources and controlling inventory. Additionally, it streamlines immediate follow-up care and improves patient satisfaction by utilizing automated reminders and scheduling functions.

Challenges and Opportunities
While Generative AI shows promise, it faces multiple challenges that must be addressed to integrate successfully into the healthcare industry.
1. Data Privacy Concerns
Utilizing Generative AI in the medical field entails handling sensitive patient information, which raises significant concerns about data privacy. Robust data protection measures are essential to maintaining patient trust and complying with regulations. Data privacy relies on data anonymization and secure data-sharing protocols to safeguard patient information.
2. Accuracy and Human Oversight
In the medical field, the accuracy of AI-generated insights is essential due to the potential repercussions of errors. Rigorously validating and supervising Generative AI models with human oversight is necessary to guarantee their reliability. Developing models that integrate smoothly with clinical decision-making procedures while maintaining high levels of accuracy is a significant challenge.
3. Regulatory Complexity
Understanding and adhering to the intricate regulation environment poses a significant challenge for GenAI implementation. Healthcare providers need to follow multiple compliance requirements when integrating AI solutions. It is crucial to deal with regulatory issues to implement Generative AI in the healthcare sector successfully.
4. Talent Readiness
AI engineers, data scientists, and software developers are among the specialists necessary to implement generative AI solutions successfully. More skilled professionals is needed to ensure model training, testing, and validation. Investing in the growth and education of talented individuals is essential for surmounting this obstacle.
5. Innovation and Model Adaptation
Organizations must innovate to address challenges related to infrastructure, computing power, and scalability required by Generative AI models. Developing smaller, specialized models tailored to specific healthcare needs can mitigate concerns related to accuracy and bias.
Future of Generative AI in Healthcare
The future of Generative AI in healthcare is promising, as multiple important areas will influence its effects.
1. Enhanced Diagnostics and Precision Medicine
Generative AI can enhance diagnostics and precision medicine by producing precise medical images and tailored treatment plans. Cutting-edge models will accurately recognize and explain diseases with unmatched precision, leading to improved and targeted therapies.
2. Collaborative AI and human interaction
The future of Generative AI involves developing collaborative environments where AI works together with healthcare professionals. Utilizing the strengths of both humans and AI will enhance clinical decisions and patient care through their interaction.
3. Integration with Big Data and Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
There are great opportunities when combining Generative AI with extensive data and electronic health records. AI models will learn from diverse data sources, identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize treatment strategies. This integration will support better coordination and continuity of care.
4. Multi-Modal Generative AI
Future trends in Generative AI involve investigating multi-modal techniques that combine different types of data, including genetic information, medical records, imaging, and sensory data. This comprehensive approach will offer a more thorough comprehension of patient well-being.
5. Continual Learning and Adaptive Systems
Generative AI systems will utilize ongoing learning methods to adjust to fresh data, emerging illnesses, and changing healthcare procedures. This flexibility allows AI models to refresh their knowledge and produce increasingly precise results as time goes on.
The possibilities outlined above merely scratch the surface of what Generative AI can achieve in healthcare. It’s a field with a promising horizon and lots of room for innovation and discovery.
Conclusion
Imagine a future where Generative AI revolutionizes the healthcare sector. Diseases are diagnosed with unparalleled accuracy, individualized treatment plans are devised to meet each patient’s unique needs, and new medications are being developed rapidly. This vision of the future is not a distant, utopian society; it can be realized through the groundbreaking capabilities of Generative AI.
When exploring the capabilities of Generative AI, it is crucial to address challenges and ethical concerns head-on. By working together, researchers, developers, and healthcare professionals ensure the ethical and responsible deployment of Generative AI for the greater good.
Are you prepared to join this healthcare transformation? Deepen your understanding of Generative AI and discover its potential to revolutionize patient care. Let’s welcome the future of healthcare as a united group.



 August 13, 2024
August 13, 2024











