Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing how businesses operate. From automating routine tasks to analyzing massive datasets in seconds, AI has transformed industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Companies use AI to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make smarter decisions with AI TRiSM.
A 2023 McKinsey report reveals that 55% of organizations now use AI in at least one business unit or function, up from 50% in 2022 and 20% in 2017.
However, as AI’s influence grows, so do concerns about its trustworthiness. Many AI models operate as “black boxes,” making decisions without clear explanations. This opacity can be problematic, especially in critical areas like hiring, lending, and medical diagnostics.
For instance, there have been instances where AI-driven hiring tools mistakeably showed prejudice against certain applicants, leading to legal and reputational challenges. Amazon scrapped its AI recruitment tool as it kept showing bias against women.
Security is also a growing concern. As AI becomes more advanced, so do the threats against it. Hackers can manipulate AI models, causing them to behave unpredictably. Cybercriminals can use AI to create more sophisticated phishing attacks or deepfake scams. Without proper safeguards, AI could become a liability rather than an asset.
Recognizing these challenges, businesses and policymakers are emphasizing AI governance. One framework gaining traction is AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management (AI TRiSM). AI TRiSM is a set of solutions designed to proactively identify and mitigate the risks that AI presents to businesses today.
Let’s explore AI TRiSM’s key components and discuss how businesses can implement it effectively.
AI is here to stay, but without proper oversight, it could create more problems than it solves. Understanding AI TRiSM is the first step toward building a future where AI is both powerful and responsible.
What is AI TRiSM, and Why Does It Matter?
AI TRiSM stands for AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management. It’s a fancy way of saying: Let’s make sure AI is reliable, fair, and safe to use.
The Problem with Unchecked AI
Let’s talk about the infamous case of Amazon’s hiring algorithm that we mentioned above.
In 2018, it was revealed that the company’s AI-driven recruitment tool was systematically discriminating against women. The system was trained on historical hiring data, which predominantly featured male candidates.
As a result, the AI learned to penalize resumes that included words like “women’s” or listed all-female colleges. Amazon eventually scrapped the project, but the incident highlighted a glaring issue: AI can perpetuate and even amplify human biases if not properly managed.
Now, this isn’t an isolated example. In 2020, an investigation by The Markup found that algorithms used by major lenders were charging higher interest rates to Black and Latino borrowers, even when their financial profiles were similar to those of white borrowers.
Similarly, facial recognition systems have been shown to misidentify people of color at significantly higher rates, raising concerns about their use in law enforcement.
Why AI TRiSM Matters
AI TRiSM addresses these challenges by focusing on three key pillars: trust, risk, and security.
Trust: For AI to be widely adopted, people need to trust it. This means ensuring that AI systems are transparent, explainable, and free from bias. Tools like explainable AI (XAI) are being developed to help users understand how decisions are made, fostering greater accountability.
Risk: AI systems can fail in unpredictable ways, and the consequences can be severe. For instance, a biased algorithm could deny someone a loan or a job opportunity, while a flawed medical AI could misdiagnose a patient. AI TRiSM helps organizations identify and mitigate these risks before they escalate.
Security: As AI systems become more integrated into critical infrastructure, they also become targets for cyberattacks. A hacked AI system could be manipulated to make harmful decisions or leak sensitive data. AI TRiSM emphasizes robust security measures to protect against such threats.
The Growing Need for AI Governance
The stakes are only getting higher. According to the 2023 report by Gartner we mentioned above – by 2026, organizations that operationalize AI transparency, trust, and security will see their AI models achieve 50% better results in terms of adoption, business goals, and user acceptance.
Now Governments are also stepping in. The European Union’s proposed AI Act aims to regulate high-risk AI systems, requiring companies to demonstrate compliance with strict transparency and safety standards.
AI TRiSM isn’t just a technical necessity—it’s a moral imperative
As AI continues to reshape industries and societies, we must ensure that it serves everyone fairly and responsibly. Without proper trust, risk, and security management, the promise of AI could quickly turn into threat.
By adopting AI TRiSM frameworks, organizations can not only avoid costly mistakes but also build AI systems that are ethical, transparent, and secure.
After all, the goal isn’t just to create smarter machines—it’s to create a smarter, fairer world.
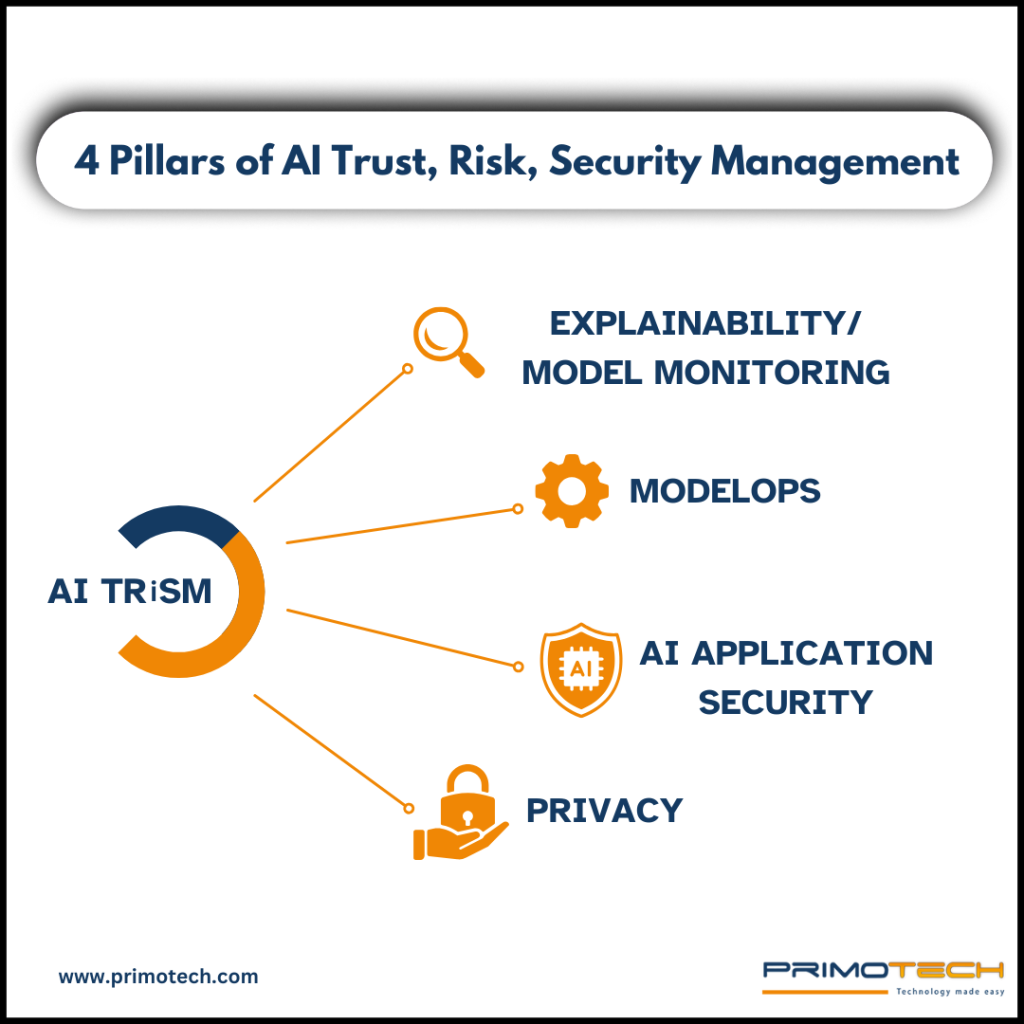
To make AI trustworthy and secure, businesses follow four key principles. Think of these as the building blocks that ensure AI systems are fair, transparent, and safe. Let’s break them down one by one:
1. Explainability & Model Monitoring
AI should never feel like a mysterious black box. If an AI system makes a decision, users—whether they’re doctors, bankers, or everyday people—need to understand why.
For example, imagine you apply for a loan, and the bank’s AI rejects your application. Wouldn’t you want to know the reason? Maybe it’s because of your credit score, or perhaps there’s a mistake in the data. AI TRiSM ensures companies use explainable AI, which means they can clearly explain how decisions are made.
Google’s AI Pathways Language Model (PaLM) can now explain its reasoning for medical diagnoses in a way that doctors can understand. This helps build trust and ensures that AI is used as a helpful tool, not a confusing one.
2. ModelOps (AI Lifecycle Management)
AI isn’t a “set it and forget it” tool. It needs regular maintenance to keep running smoothly. ModelOps is all about managing AI systems throughout their lifecycle, from development to deployment and beyond. This includes monitoring performance, updating models, and ensuring they stay accurate and ethical over time.
Tesla’s Autopilot system is a great example, every few months, Tesla releases updates to improve its self-driving AI based on real-world driving data. Without these updates, the technology could become outdated or even dangerous. ModelOps ensures AI systems evolve and stay reliable.
3. AI Application Security
AI models can be hacked, manipulated, or fooled if they’re not properly protected. This is a big deal, especially when AI is used in critical areas like healthcare, transportation, or finance.
For instance, in 2023, researchers tricked an AI by changing just a few pixels in an image. The AI misidentified a stop sign as a speed limit sign—a small change with potentially huge consequences, especially for self-driving cars.
How AI TRiSM helps?
It focuses on protecting AI from cyber threats using techniques like adversarial training (teaching AI to recognize and resist attacks) and secure data handling. This ensures AI systems can’t be easily fooled or hacked.
4. Model Privacy & Compliance
AI often deals with sensitive data—your medical records, financial details, or even personal messages. Without proper privacy measures, this data could be leaked or misused.
Apple’s Face ID – Instead of storing your face scan in the cloud, it keeps it securely on your device. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures your privacy is protected.
Governments are also stepping in to regulate AI. The European Union’s AI Act is one of the first laws aimed at ensuring AI systems are safe, transparent, and compliant with privacy standards.
The Real Benefits of AI TRiSM
By following these four pillars, businesses can build AI systems that are not only powerful but also ethical and trustworthy. Here’s what AI TRiSM brings to the table:
Transparency: Users understand how decisions are made, building trust in AI systems.
Reliability: Regular updates and monitoring ensure AI stays accurate and effective.
Security: Protects AI from cyber threats and manipulation.
Privacy: Keeps sensitive data safe and ensures compliance with laws.
In short, AI TRiSM isn’t just about avoiding problems—it’s about creating AI that works for everyone, fairly and safely.
The Trust Factor: Why AI Needs to Be Explainable
Imagine you’re applying for a loan, and the bank denies your application. If the decision came from an AI system, you’d probably want to know why. Was it your credit score? Your income? Without a clear explanation, you’d be left guessing. This lack of clarity can make people lose trust in AI systems.
Transparency in AI means being open about how these systems work. It’s about showing the steps and data an AI uses to make a decision. When companies are transparent, users feel more comfortable and are more likely to trust the technology.
Black-Box AI vs. Explainable AI (XAI)
Not all AI systems are easy to understand. Some are like “black boxes,” where data goes in, a decision comes out, but the process in between is a mystery. This can be a problem, especially in areas like healthcare and finance, where understanding the reasoning behind a decision is crucial.
Explainable AI (XAI) aims to open up this black box. It provides clear reasons for its decisions, making it easier for humans to understand and trust the outcomes. For instance, if an AI recommends a medical treatment, XAI can show which symptoms and test results led to that suggestion.
Use Cases: How Hospitals and Banks Benefit from AI Explainability
In an article, in MedCity News, Lars Maaløe, explained how in the healthcare sector, doctors are using AI to help diagnose diseases, and how they need to trust these tools.
He explained, how if an AI suggests a diagnosis, explainability allows the doctor to see which symptoms and data points led to that conclusion.
This collaboration ensures patients get accurate and reliable care.
Similarly, in the finance sector, as mentioned in an article in Binariks, banks are using AI to assess loan applications. An explainable AI can show applicants why they were approved or denied, detailing factors like credit history or income levels.
This transparency helps customers understand their financial standing and builds trust in the bank’s processes.
The Growing Threat of AI Cyberattacks
Hackers have started focusing on AI models because they process massive amounts of sensitive data. From personal details to financial records, AI systems store and analyze information that cybercriminals can misuse.
The most common ways hackers attack AI models include manipulating input data, extracting valuable models, and using AI itself to launch sophisticated attacks.
AI-Powered Phishing, Adversarial Examples, and Model Extraction Attacks
AI-Powered Phishing: Phishing attacks have been around for a long time, but AI has taken them to a new level. Hackers now use AI to create highly convincing fake emails, messages, and even deepfake videos. These AI-generated phishing scams can trick employees into sharing sensitive data or downloading malware.
Adversarial Examples: AI models, especially those used in image recognition and cybersecurity, can be tricked by tiny, imperceptible changes in input data. For example, a hacker can alter a few pixels in an image, causing an AI model to misinterpret it completely. In the real world, this could lead to AI security cameras failing to detect intruders or self-driving cars misreading road signs.
Model Extraction Attacks: Some hackers try to reverse-engineer AI models by repeatedly interacting with them and gathering enough data to reconstruct their functionality. Once they’ve copied the AI model, they can exploit its weaknesses or use it to launch attacks on the original system.
Steps Companies Can Take to Prevent Cyber Risks
Using AI to Detect Threats: Leveraging AI-powered cybersecurity tools that can identify suspicious activities and block attacks before they cause damage is a great start.
Encrypting AI Models and Data: Encrypt AI training data to ensure that even if hackers gain access, they won’t be able to use the information.
Running Adversarial Testing: Security teams should test their own AI models by trying to attack them—this helps identify weaknesses before hackers do.
Implementing Strict Access Controls: Restrict access to AI systems, making it harder for unauthorized users to manipulate models.
AI security is a growing challenge, but with the right protections in place, businesses can stay ahead of cybercriminals and ensure their AI remains safe and reliable.
Privacy and Ethical AI: Keeping User Data Safe
AI systems process vast amounts of user data—everything from search history to health records. While this helps improve AI’s accuracy and usefulness, it also raises big concerns about privacy and ethics.
How AI Collects and Processes User Data?
AI learns from data. Whether it’s a voice assistant recognizing your speech or an e-commerce platform recommending products, AI models analyze your behavior to make predictions. But where does this data come from?
Web and App Tracking: AI collects data from websites, mobile apps, and social media interactions.
CCTV and Facial Recognition: AI-powered surveillance systems store facial data to enhance security.
Healthcare Records: Hospitals use AI to process patient data and predict health risks.
If not handled properly, this data can be misused, leading to security breaches or privacy violations.
Ethical Concerns and Data Privacy Laws (GDPR, CCPA)
Many AI systems operate without users fully understanding how their data is used. This raises ethical concerns such as:
Lack of Consent: Some AI-driven platforms collect user data without clear permission.
Bias in AI Decisions: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to unfair treatment in areas like hiring, banking, and healthcare.
Surveillance Overreach: AI-powered surveillance tools can track people’s movements without their knowledge.
To address these concerns, governments have introduced strict data privacy laws:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (Europe): This law requires companies to get explicit user consent before collecting personal data and gives users the right to delete their information.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) (U.S.): CCPA gives users more control over their data and allows them to opt out of being tracked.
These laws are pushing companies to be more transparent about how they handle user data.
How AI TRiSM Ensures Compliance
AI TRiSM helps companies comply with privacy laws by:
Providing Explainability: AI models need to clearly explain how decisions are made, so users understand how their data is used.
Ensuring Fairness: Companies must test AI systems for biases and correct them before deployment.
Automating Compliance Checks: AI TRiSM tools can automatically flag privacy violations and suggest fixes, ensuring organizations stay within legal guidelines.
Use Case: AI Privacy in the Healthcare Sector
The healthcare industry relies heavily on AI for diagnosis, patient monitoring, and drug development. But handling sensitive medical data comes with risks.
Take, for example, AI-driven diagnostic tools used in hospitals. These tools analyze patient symptoms and suggest possible conditions. If this data isn’t properly secured, it could be exposed in a data breach, leading to serious privacy violations.
To combat this, hospitals and healthcare companies are adopting AI TRiSM strategies such as:
Anonymizing Patient Data: AI models are trained on medical data without storing personally identifiable information.
Secure Cloud Storage: Healthcare providers are using encrypted cloud solutions to store AI-generated insights safely.
Strict Access Controls: Only authorized personnel can access AI-driven medical records, reducing the risk of data leaks.
The Challenges of Implementing AI TRiSM
AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management (AI TRiSM) is a game-changer in ensuring AI remains secure, ethical, and reliable. But implementing it is easier said than done. Many businesses struggle with cost, technical limitations, and resistance to change.
Common Roadblocks: Cost, Technical Limitations, and Resistance to Change
Cost – AI TRiSM requires investment in security infrastructure, compliance frameworks, and skilled professionals. For small and mid-sized companies, these expenses can be a major hurdle.
Technical Limitations – Many AI models, especially legacy systems, were not designed with explainability or security in mind. Retrofitting AI TRiSM into existing workflows can be complex.
Resistance to Change – Employees and decision-makers may hesitate to adopt AI TRiSM due to a lack of awareness or fear of disrupting existing operations.
Strategies to Successfully Implement AI TRiSM
Start Small, Scale Gradually – Instead of overhauling everything at once, businesses should start by implementing AI TRiSM in high-risk areas like fraud detection or customer data security.
Invest in AI Governance Tools – AI security and compliance platforms can help automate risk monitoring and detect vulnerabilities early.
Educate Teams on AI Ethics – Employees need to understand why AI TRiSM matters and how it impacts business decisions. Training programs can help bridge the knowledge gap.
Collaborate with AI Security Experts – Partnering with AI security firms like Primotech can provide you with the expertise needed to navigate complex AI governance challenges.
The Future of AI TRiSM: What Lies Ahead?
So what are the emerging risks, the role of quantum computing, and how businesses can future-proof their AI systems?
Emerging AI Security Threats
AI-Powered Cyberattacks – Hackers are using AI to launch automated, highly sophisticated attacks that can bypass traditional security measures.
Data Poisoning – Attackers are manipulating training data to corrupt AI models, making them biased or ineffective.
Deepfake Scams – AI-generated deepfakes are being used in fraud schemes, making it harder to distinguish real from fake.
The Role of Quantum Computing in AI Risk
Quantum computing has the potential to break existing encryption methods, posing a huge risk to AI security. While still in its early stages, companies need to start preparing by:
Exploring quantum-resistant encryption to protect AI models.
Investing in AI-driven threat detection to identify quantum-related risks early.
Staying updated on quantum computing advancements to adapt before it becomes a widespread threat.
How Companies Can Future-Proof AI Systems
Adopt AI TRiSM Frameworks Now – Waiting until a crisis happens isn’t an option. Companies need to integrate AI TRiSM into their workflows today.
Stay Ahead with Continuous Monitoring – AI models must be regularly tested and updated to prevent vulnerabilities.
Leverage AI to Secure AI – Businesses should use AI-driven security tools that can predict and counter threats in real time.
How Primotech can help with AI Security and Governance
At Primotech, we specialize in AI security, risk management, and ethical AI governance. Our AI and Data Governance team helps businesses:
Build AI systems that are secure, transparent, and compliant.
Detect and prevent AI-powered cyber threats before they cause damage.
Implement AI governance strategies that ensure fair, unbiased, and responsible AI.
Don’t wait for an AI crisis to act—secure your AI today. Contact us to learn how we can help your business navigate the future of AI safely!



 February 20, 2025
February 20, 2025