If you are a business owner with an online presence, you must have heard about Google updates. One of the largest search engines globally, Google holds over 92% of the market share compared to the competition.
Recently, Google has dropped some tips and bits of information to roll out a new Core Web Vitals update from June to August 2021.
So, what is it about?
The Core Web Vitals contains 3 new metrics that track and quantify user experience on a website. It highlights the website speed as the primary metric for SEO. It will be now part of the existing page experience signals like
- Responsiveness
- Safe-browsing experience
- Intrusive interstitial guidelines
- HTTPS security
All these metrics are now going to be official ranking factors for a website. However, the relative imperativeness will be low compared to the other 200 elements on the list.Web admins should start considering these signals for the website user experience audits and ensure their website loads faster and be more stable across all devices and platforms.
Page Experience Signals
Let us break down some of the existing Page Experience Signals below for your understanding:
1. Responsiveness
It is all about making sure that your website is mobile-friendly. Whenever a user switches from a desktop version to a mobile, the site must provide a similar or better user experience to ensure a seamless and hassle-free browsing experience. You should focus on user-driven design and ensure best accessibility practices to rank better on search engines. Here are some ways you can make your website mobile-friendly:
- Reduce the load time
- Test website responsiveness in varied resolutions
- Make website navigation easy for the users on mobile
- Touch-friendly actions
- Easy to read text
- Safe browsing with less intrusive advertising (if any)
Google launched the secure browsing experience in 2007 to protect users from malicious attacks. It has widened the parameters and now protects users from phishing attacks, misleading content, and more. You can check your Search Console ( Security and Manual Actions) to review if your website has any malicious infiltration.
2. HTTPS-security
It is now a primary requisite for a site. It shows that the site is secure and ensures secure communication (SSL/TLS secures). It is a benchmark for the security of user data while browsing or communicating on a website. It ensures that user data cannot be modified or stolen during user and server interaction.
If your site is still using HTTP protocol, you need to know that Google considers your site insecure and will not show it to its users. You will lose ranking because of this. If you haven’t updated to HTTPS, it is time that you do so.
3. No Intrusive interstitials
Nobody likes those pop-up ads that hinder a user’s interaction with a website. So, if your site has intrusive ads, overlays on the desktop or mobile, you can lose your ranking. It is a bad practice in general and is seen as deceitful in the eyes of Google. However, you won’t get penalized for displaying pop-up ads, but if they hamper user experience and get reported, you can get blacklisted. Google provides some guidelines on what’s acceptable and what’s not!
Allowed:
- Consent-related pop-ups: cookies, age verification, etc.
- Small pop-ups that cover less screen space
Not Allowed:
- Too many ads above-the-fold (over the main content or ads that push the main content below the fold)
- Big pop-ups that hide your main content
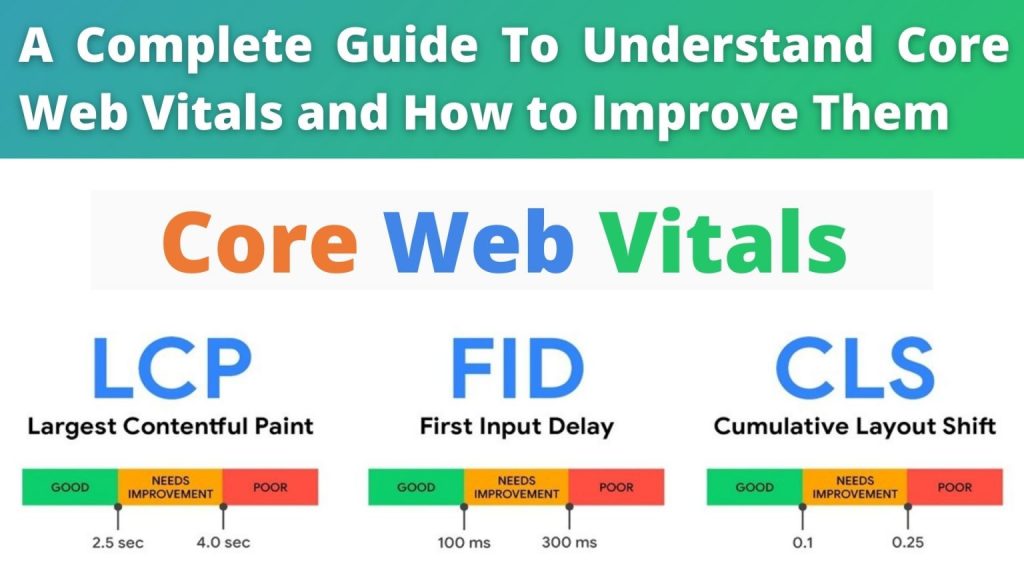
What are Core Web Vitals?
It is the newly integrated metrics that have become a significant part of Google’s Page Experience signals. They are added to help analyze, measure, and enhance user experience. The goal is to help site owners and developers to focus on the stuff that matters the most to users.
Currently, there are three metrics in Core Web Vitals that are focused on user experience. You have to keep in mind that whilst you can monitor CWV for both desktop and mobile, it is the mobile signals that work here for ranking. So if you want to ensure good ranking, your pages should meet the recommended scores for at least 75% of page visits.
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
It is a user-centric metric that measures a site’s page loading performance. It includes page load time, especially how much time it takes to load the site’s main content. It is different from First Contentful Paint (FCP) that checks and analyses first content loads. LCP is all about measuring the meaningful content – for example, a paragraph, hero image, etc. that is pertinent to the user.
LCP might be different for mobile and desktop. It is usually the largest element of the web page that users see when they visit. Note that by the largest element, we mean the actual size of the section that is not affected by CSS margin, padding, border, etc.
What can be considered a good LCP score for your site?
For your website to pass Core Web Vitals, you must target to get an LCP score of 2.5 seconds or less.
The higher your LCP score is, the more chances of an increase in bounce rate and lowers conversion rates.
What to look for to reduce LCP time?
- Large file size (unoptimized images & video)
- Render-blocking JavaScript
- Slow server load time
2. First Input Delay (FID)
This metric measures the user interactivity experience and responsiveness of the page. It analyses a user’s first impression and notices the delay in an event processing. For example, it considers when a user visits a page and clicks a button or a link and the time your site takes to respond to a particular click.
FID measures the first user interaction only as it is the most crucial factor in user experience. For pages that do not have any interaction, it won’t be taken into account. For example, scrolling and zooming on the site won’t be considered if there isn’t a CTA for a user to interact.
What can be considered as a good FID score?
Less than 100 ms is a good score to target!
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
It measures a web page’s visual stability. It monitors the layout shift when there is an accidental click by the user before the site is fully loaded. It checks whether the site layout shifts during such an encounter. The goal is to ensure that page elements stay static as they load, and an interaction can occur after the page has fully loaded.
What can be considered as a good CLS score?
It would be best if you targeted to get a score less or equal to 0.1 seconds. It means that your web page contents should be fully static during the loading. CLS usually happens due to images, ads, embedded codes, iframes, web fonts, and shoddy coding.
How can you measure and test Core Web Vitals?
As mentioned above, the new Page Experience signals and existing Core Web Vitalswill impact your ranking on both mobile and desktop. The new signals that are going to be added in this next update will be interesting to observe. There is also news that Google will stop considering AMP as a requirement for top stories on mobile.
Here are some tools to help you measure, test, and understand Core Web Vitals:
1. Field Data
It is also known as real user monitoring. It measures real users on a site, coming from various devices, networks, and historical data. This data is aggregated for your whole site. Google uses it as a ranking factor for your site. So, you must audit and inspect your real-user experience using field data.
2. Google Search Console
It has a Core Web Vitals report to help you identify issues divided by the three metrics LCP, FID, and CLS. It applies to both mobile and desktop versions of your site. You need to verify your DNS to view your website report thought!
Google will be rolling out a new Page Experience report within the Google Search Console. This will make it easy for you to evaluate site performance quickly and weed out the pages with issues.
3. Page Speed Insights
It is a browser-based site speed testing tool and includes CWV reports as well.You can evaluate your site’s performance page-by-page. Please note that the scores for desktop and mobile might differ.
4. Chrome UX Report (CrUX)
It includesreal-time chrome user experience data from millions of websites. It focuses on website loading performance and also measures Core Web Vitals metrics and more.
5. Web Vitals Extension for Chrome
This extension allows you to perform real-time analysis of the main three Core Web Vitals metrics.
6. Lighthouse
It is an open-source auditing tool that allows developers to identify site issues and improve the health of web pages. The latest version of this tool includes reports of CWV.
7. Chrome DevTools Panel
You can open this in incognito mode and press Command+Option+I (For Mac) or Control+Shift+I (For Windows, Linux). Chrome DevTools gives you a complete performance panel that includes the new Core Web Vitals.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals
Once you have analyzed your site using one of the tools I have mentioned above, it is time to fix and improve the stats.
Improving LCP and FID
Go for a Fast and Reliable Web Host: If you have a lousy LCP score, it could be due to a slow server response time. Firstly, check your TTFB score. It tells how much time it takes for the browser to receive the first bits of content from the server. A faster server response time will automatically ensure a quicker site load.
1. Allow full-page caching
It allows your site’s page content to be stored on the server as an HTML version after the first load. Once your site has been visited, the first load will be from the database. The concurrent loads will be directly from the server’s memory, making your site load much faster and improving your LCP metric.
2. Defer JavaScript
It is one of the most addressed issues. A browser takes time to load the JavaScript, which in turn delays the loading of the whole page and user interaction. So if you haven’t deferred your JavaScript, the browser will process and load JS files after parsing the HTML.
3. Minify CSS and JS files
It is the best practice to offer easy readability to users. Minification optimizes all the junk in the code by removing unnecessary characters and help in producing faster render time.
4. Optimize browser caching
It is an efficient way to load site elements faster. For example, the website images, data, and elements are stored in the user’s browser the first time. From next time onward, the site loads directly from the browser, making the page load faster. So, it would help if you allowed the static files to be cached.
5. Purchase a CDN
You can use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your image loading on web pages. The CDN caches all your content across a global network of high-performance servers. So, whenever a user from anywhere around the globe visits your site, it loads your content from a server closest to the visitor. This improves load time and user experience significantly.
6. Remove third-party scripts
You should remove all third-party scripts from the site that doesn’t provide real value to your website. The scripts that are not intertwined with your site code or that you don’t use anymore should be removed. It will improve your LCP and FID score.
7. Optimize your images
Some good practices to optimize your images are:
- Compression without losing quality: You can use many tools to compress your image size without losing quality. This improves your loading time.
-
- Upgrade image formats: Start upgrading your web images to next-gen formats like JPEG 2000, JPEG XR, and WebP. Google recommends WebP format.
- Scale images correctly: This is important as it confirms responsiveness across platforms and browsers.
- Add Lazy loading: You can add lazy load to your static content. But keep in mind to exclude lazy load from your LCP elements.
- Let go of the old hero slider images above the fold.
Improving CLS
1. Designate a space for your ads on the site
You must place your website ads carefully. While we understand the dynamic nature of ads and how it provokes interaction from users, it can also lead to unexpected CLS. It adversely affects your CLS score. So, have a designated space for the ads, so they don’t ruin the user experience.
2. Optimize your fonts
Don’t go overboard with varied fonts. Choose your website font carefully. It improves the readability of your page and conveys your brand’s image. However, fonts are an additional resource. So, if you have too many font styles on your page, it can slow down the load time. It is recommended to optimize the fonts and preload them to avoid a layout shift while loading.
3. Set size attribute dimensions
Whether it is videos, images, GIFs, infographics, etc., you need to set the size attribute dimensions for the media. It will communicate to the user’s browser about how much space a particular element on your page needs. It will reduce Cumulative Layout Shifts.
Conclusion
The Core Web Vitals metrics and their scoring conditions may change in the coming years. For sure, Google is going to keep tweaking the current metrics to benefit user experience. While the actual content on the site is still going to be the most significant factor for your ranking, ensuring a good Core Web Vitals score qualifies your site for search engine ranking. It can even give you a competitive edge.
Need help with improving your Core Web Vitals? Get in touch with us!



 June 7, 2021
June 7, 2021










